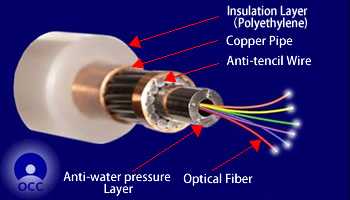
- Structure of light weight optical submarine cable
Technology Introduction
Optical Submarine Cable
There are basically two types of optical submarine cables. One is a light weight cable, and is used in deep sea areas of around 1,000m to 8,500m depth. The other is an armored cable being attached a steel wire to the light weight cable, and is used in a shallower area than about 1,000m depth.
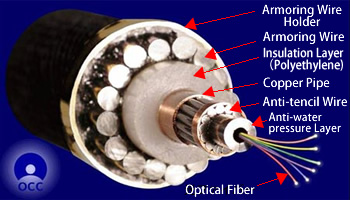
- Structure of single armored submarine cable
Optical Submarine Cable Laying Method
KCS is realizing the construction of cable laying with high quality and high reliability by performing the followings:
(1)Designs the most suitable speed of the cable payout and the ship, considering the water depth along with the cable laying route, ups and downs of the seabed and the types of the laying cables.
(2)Operates the cable handling facilities such as the cable engines or the ship's navigation system precisely according to the design.
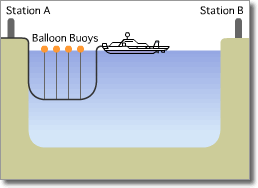
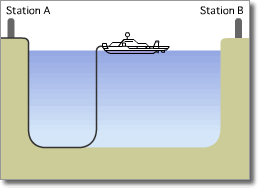
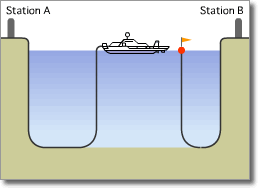
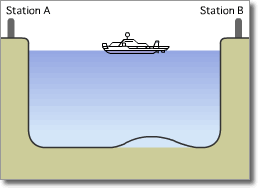
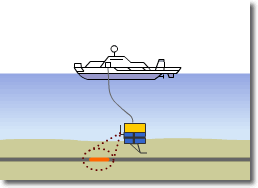
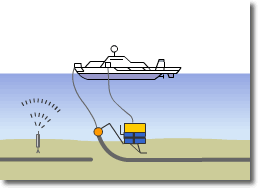
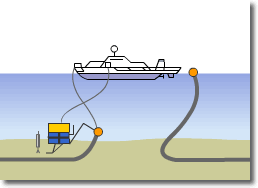
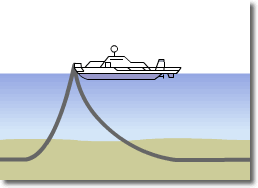
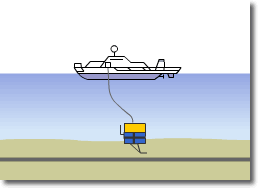
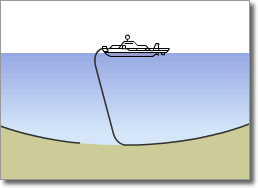
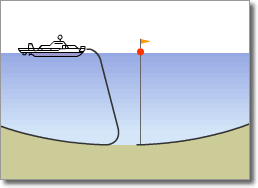
Optical Submarine Cable Laying Procedure
Optical Submarine Cable Burial Method
In the water area shallower than the depth of 1,000 meters, cables are buried under the seabed mainly by two ways in order to protect them from damages, which might be caused by fishing activities or anchors of large vessels.
The one is to use the towed type burying machine, PLOW-II, which performs the simultaneous operation of cable laying and burial.
PLOW-II makes the installation period shorter because of the simultaneous operation of cable laying and burial, and is suitable for new and long distance operations.
Since PLOW-II is towed by the vessel on the seabed after threading the cable through it, it cannot be used for the burial operation after laying(burial after laying).
The working area of PLOW-II is limited depending on the seabed form or the slope.
The other is burial by ROV(MARCAS-IV, MARCAS-V).
ROV digs, by blasting waterjet into the seabed, a trench with the targeted burial depth by coming and going several times at the same section, and drops the cable into the trench. Because of this method, the construction efficiency of ROV is not better than PLOW-II. However,
ROV has the capability that it can float and move around on the sea bed, and ROV can work for the carved cable section which was caused by the final bight release, or in the area where PLOW-II can not be operated due to severe condition of the seabed.
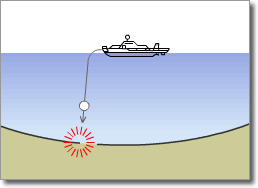
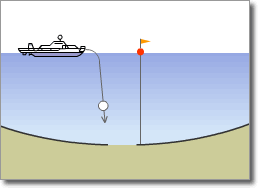
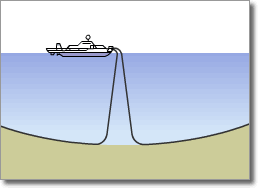
Example of Cable Searching and Burial after Laying by ROV
Optical Submarine Cable Repair Method
There is a case in which an optical fiber cable is cut or damaged due to ocean earthquakes and fishing gears etc..
In the situation, the cable ship is urgently dispatched to the cable failure site and repairs the cable.
The cable repair procedure normally consists of the followings:
1) Localization of the cable failure point.
2) Recovery of the failure cable onto the ship
3) Cutting and removal of the cable failure section
4) Jointing of the recovered cable and the spare cable in the cable tank of the ship
5) Confirmation test and reburial of the cable
 KDDI Cableships & Subsea Engineering Inc.
KDDI Cableships & Subsea Engineering Inc.